Intervention By Design Data Management Tool
According to a 2020 Experian report on data management, 85% of organizations see data as one of the most valuable assets to their business. However, most companies are struggling to manage it. There are dozens of concepts and variables around data management, which can get confusing. That's why, before exploring some of those key definitions, let's bust some myths around data management: Now that you know that everyone can benefit from data management, let's talk about what it is, why it's so important (and sometimes so difficult) to get right, best practices, and top vendors for different business sizes. Data management is the practice of collecting, storing, protecting, and processing data in a way that's sustainable and effective. In business, data is usually associated with customers, prospects, employees, providers, deals, accounts, competitors, and finances. When an organization effectively manages data, they gain insights that drive business decisions. Data management encompasses three basic stages: collection, storing, and processing. However, protecting your data should be a priority throughout the entire process, especially as data privacy concerns rise and ransomware attacks become rampant. Since business applications and the databases within them come in all sizes, each company should take its own approach to these stages. You should do so considering your particular technology ecosystem and, if necessary, define and add new steps to the process. Data cleansing, for instance, might be a small and short step for a startup with limited data whereas an enterprise-level company might need to prioritize it early on in the process. For every media dollar spent in marketing, 21 cents are wasted due to poor data quality, according to a 2019 Forrester study. In addition to the financial cost, poor data management leads to poor customer experiences. If you can't rely on your data to provide accurate insights, then you're not able to design strategies that will be effective for your target audience. With this in mind, marketing teams must prioritize data management at every stage of their growth. While there are techniques and best practices that can help you manage data, there's no one-size-fits-all data management plan. There are, however, guidelines on how to set up your management strategy. More on that in the next section. Every day, your business collects data. So much data, in fact, that you need an action plan on what to focus on to move forward. Your action plan will stem from the objectives you've set as a company. For instance, let's say your company's main goal for the next year is to grow your client base by 20%. With this in mind, what type of insights will be most valuable? What data should you be collecting and focusing on? Having a clear goal will serve as your anchor as you determine your process and tools down the line. Once you know what your goals are, it's time to get into the nitty-gritty details. As mentioned before, data management comprises three main activities: collecting, storing, and processing (or analyzing). At this point, you'll want to figure out the tactical steps needed to perform each activity. For data collection, you'll want to know: As for the storing process, where and how will your data be stored? What security protocols do you have in place? How will you organize unstructured and structured data? When it comes to processing your data, it's important to know who will be responsible for it. If you have a large team, you may have business intelligence analysts who can pull or generate reports. The next step in developing your data management strategy is finding the right technology to support your efforts. With so much data to sort through, it's nearly impossible to do it manually. You may rely on Excel sheets for a while but even those can prove to be faulty and unsustainable. Look for software that is suited to your business size and leaves room for it to grow. More on that here. Think of your governance standards as your standard operating procedures as it pertains to data management. It determines what actions can be taken, by whom, and when for all things data. Why do this? It streamlines your data collection and integration process by ensuring that everyone is following the same formula. This framework also promotes accountability and creates a sustainable structure from which to grow your management strategy over time. Lastly, data governance means cleaner data, which will enable better business decisions. According to Forbes, "the gold is now data," and they predict that by 2025, the global market for data and data analytics will be worth $135 billion. Top business managers are willing to invest in data because of its indisputable value. But there's a catch: data can be very difficult to manage properly, especially if you didn't start thinking about data management at an early stage of your company. Then, you might end up with an enormous amount of data in a completely unmanageable format. With this in mind, it's important to prioritize the following data goals every organization should have. Data integrity is determined by how consistent data is. Having data integrity requires a smart data collection process. When filling out a web form, have you ever misspelled your phone number and gotten a message saying something like "The phone number you added is incorrect, please try again"? Form validation is a clear example of one of those "smart collection processes," that are created to make sure the data you are gathering is valid. Other ways to ensure data integrity include: Data quality is one of the main obstacles companies face today. In a 2021 Experian study, over 50% of business leaders say they don't fully trust their data assets. When talking about high-quality data, there are three concepts to highlight: accessibility, consistency, and relevance. Thomas Redman, in his book Data Driven: Profiting from Your Most Important Business Asset, frames the concept of data quality well by saying that data is high quality if it is "fit for its intended uses in operations, decision making, and planning." Here's how it works: Once you achieve data integrity, you'll have consistent data. But if that data is not accessible when you need it, it doesn't suit its intended purpose. Similarly, if data is consistent and accessible but not relevant for your operations and objectives, it also loses its quality. The average company draws data from various sources and software, including their CRM, and CMS. That's why software integration is one of the biggest data challenges your company might face. Each one of your applications has a database with particular characteristics and doesn't always connect natively with your other apps. However, to have a complete overview of your data, you need to unify your software stack. Integrations can be as complex as they are necessary. But fortunately, with the rise of Integration Platforms as a Service (iPaaS), like Operations Hub, you can have a single platform that serves as your source of truth for accessible, clean, and reliable data. Managing data has to be taken seriously, especially if you are working with your customers' data. Not following the compliance requirements established locally and internationally can have serious legal ramifications. Not to mention the loss of consumer trust. As a business, you have the responsibility to keep up with compliance requirements and ensure the proper management of data. Over the last few years, at least three major data regulations have been implemented: the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Data Protection Act 2018, and the California Consumer Privacy Act. There's a lot to keep in mind when you want to implement or improve your company's data management. The good news is that lots of companies like yours are successfully managing their data and you can learn what has worked for them. Your company's data management plan or strategy will always depend on your unique software stack, database, and company size. However, the following best practices and techniques are good starting points to adapt and customize based on your needs. Vendors like Google offer data catalogs as a complementary product for data management. These products are essentially search bars to make data assets easy to find and categorize. If you are running a small business, you can replicate the function of data catalogs by creating an inventory of all the data assets your company has. This data catalog can help your different teams easily find the data they need to access. Tags and labels are a great way to categorize groups of data to find them easily later on. Having a clear and complete inventory of your data assets is also very useful when you want to build workflows or integrations between databases. Here's an example from HubSpot's Operations Hub. Image Source Data is rarely collected by a single platform. Usually, there are several applications in place for specialized processes or operations that each have their own databases and gather a fragment of your company's data. Let's say you have an online shop where you sell running shoes. You might have one app gathering the information your customers fill out when they make a purchase, a second app for billing or accounting, and perhaps a third one with a chatbot to answer questions. All these apps collect a piece of data about one single customer. The goal of integration is to keep all those fragments together and offer a single customer view (SCV). When data is integrated, its quality improves and allows you to track users throughout the entire customer journey. If your company is working with in-house software applications, integration might require a team of engineers with an ad-hoc solution. For those small and medium-sized organizations that work with cloud-based platforms, iPaaS can be a great solution. Data lifecycle management (DLM) is mostly used by big companies working with massive amounts of data that need to be categorized into tiers, often with complex automation. For smaller businesses, it can also be a useful structure to keep in mind while you are developing a strategy for data management. In simple terms, DLM identifies the different stages that information flows through and creates policies to manage each one of those stages. The ultimate goal of this framework is to maximize the useful life of your data. The stages or steps of DLM are: Data warehouse and a customer data platform are two of the most common ways data is collected and stored. A data warehouse is a database to which a company transfers all of its data – usually from disparate sources. Data warehouses are often called data lakes or data marts. You may also be familiar with the term enterprise data warehouse (EDW), which is designed with larger companies in mind. A customer data platform is a more user-friendly platform that also collects data relevant to your customers and displays the data to end-users in tailored, visual reports. Often, a customer data platform is simply the 'front end' of a behind-the-scenes data warehouse. In both cases, a business may take all the data from its CRM, help desk, web analytics, financial, and other internal systems to store it in a designated location. When it comes to data management, there are software designed for startups to large-scale enterprises, focusing on the different operations and stages of data. Often, the same vendor will offer several products to manage one or more operations. Such is the case of Oracle, IBM, SAP, or Microsoft with its Azure services. Among the most popular all-encompassing solutions, you'll find master data management software (DMD), storage, and integration services – key features for large-scale businesses. This type of software typically includes solutions for data consolidation, cleansing, accessibility, verification, and organization. Here are some of the most popular tools around: SAP's software helps you consolidate, enrich, process, and analyze your master data. This product is often complemented by the brand's Master Data Governance tool. Ataccama specializes in several data stages and operations, offering a data stewardship service with an accessible data catalog and even some artificial intelligence (AI) features. These services help you manage your storage capacity in a cost-effective way. The four types of storage management are cold storage, block storage, cloud file storage, and hybrid cloud storage. In this context, a 'block' is a unit of data with a specific volume. It's basically like buying different USB flash drives (extremely big USBs) where you have room to store a certain volume of data. Amazon's EBS allows you to choose between four different volume types. Their software is easy to use, scalable, and cost-effective. Anyone with a Google Workspace account has access to the basic Drive version with 30 GB storage capability. On the Business and Enterprise versions of GSuite, you can get up to 25 TB of cloud storage. Because it's so easy to use, accessible, and compatible with all the other GSuite applications, Drive is a great storage management tool for small businesses. For Microsoft users, OneDrive is a reliable and affordable solution. It offers up to 6 TB and it works smoothly with the MS Office productivity suite. Plus, Microsoft is known for taking data security very seriously, and OneDrive is no exception to its security protocols. This product is ideal for businesses in the sales industry. RevOps hosts powerful tools to help businesses scale their sales operations. Features include native integrations with CRMs and API building tools. It's never too early to start thinking about data integration. The sooner you define and implement a software integration plan, the better. If the solution you need is not available natively or in-app, these are some iPaaS to consider: With its diverse features, Operations Hub serves from small businesses to enterprise-level operations teams. Next to the basic two-way sync, its starter plan offers custom fields mapping and advanced filtering for different types of data. Its complete synchronization solution works two-way and in real-time. It also works with historical data to avoid duplicates or gaps in information. It's great for one-way, one-time actions. You can set up a zap to make sure that whenever you add a new piece of data into app X, there's a copy of that piece of data in app Y. It works with several objects such as contacts, Trello cards, Slack message, Google Sheets data, etc. This integration option can help you create complex workflows between apps. For instance, if you want to get a notification on Slack every time someone subscribes to your newsletter, Automate.io is the tool for you. It's ideal for one-way and one-time workflows between the 100 apps they support. Now that we've covered a number of common concepts and definitions of data management, here are some of the benefits of investing in proper data management practices. In the book "The Inside Advantage," author Robert H. Bloom asserts that one key to business success is understanding the customers who are most profitable and whom you enjoy working with most. For a modern technology business, that answer may be easier said than done. You can't simply look at which customers spend the most money with you. You also need to assess the cost of supporting those customers, which likely comes from your help desk software and potentially your payroll system. Additionally, larger customers likely cost more to acquire - that data point comes from your CRM, marketing automation, and advertising platforms. Only when you put all of these together can you fully understand and identify your most profitable customers. When it comes to acquisition costs, it's important to understand which channels are worth re-investing in and which ones should be shelved. A data warehouse allows you to connect your customer acquisition costs with your customer retention data and understand your full ROI. In most cases, customers typically don't simply click on an ad and immediately purchase your product, especially in B2B. There is a buying cycle that can last months. In an enterprise funnel, your company is typically reaching your customers via email, ads, phone calls, nurture emails, trade shows, in-person meetings, demos, and more. It's an extremely complex process that can only be connected (and understood) by managing data properly. Data Migration: The process of moving data from one database to another. Extract, Transform, Load: A process that involves pulling data from a database (extraction), manipulating it via code in some way (transformation), and writing it back to a database (loading). Metadata: Data that describes other data within a database or data warehouse. Fact Tables: Tables containing core business metrics that have been prepared to be user-friendly and digestible for all stakeholders. These are often called "single sources of truth." Business Intelligence: The practice of analyzing and presenting data in a way that provides insight into making business decisions. Often the product of a business intelligence team is a metrics dashboard or a report with insights. Schema: The structure that defines how a database is organized. Data Cleansing: The process of detecting and correcting corrupt, inaccurate data. Data Governance: The rules and procedures that define how a company's data is managed. Often a team or individual will be responsible for data governance, and that person will be responsible for things such as access requests, definitions of column names, and maintenance of database records. Data testing: The practice of making assertions about your data, and then testing whether these assertions are valid. This concept can be used to test both the quality of your source data and to validate that the code in your data models is working as intended. Data is at the core of your business. Whether you are an entrepreneur or if you are part of a big company, a basic notion of data management can help you increase your productivity, improve your customer experience, and make life easier for your employees. There's not a single data management plan that fits all businesses, but there are dozens of options for each business. That's why, you need to understand your company's needs, its applications, and the data within them to find the right solutions for you. Editor's Note: This post was originally published in October of 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness. 
What is data management?
Data Management in Marketing
Enterprise Data Management Strategy
1. Identify your business objectives.
2. Build data processes.
3. Find the right technology.
4. Set governance standards.
Data Management Goals
Ensuring Data Integrity
Achieving Data Quality
Integrating Disparate Databases
Complying with Ever-Changing Compliance Requirements
Data Management Best Practices
Data Catalogs
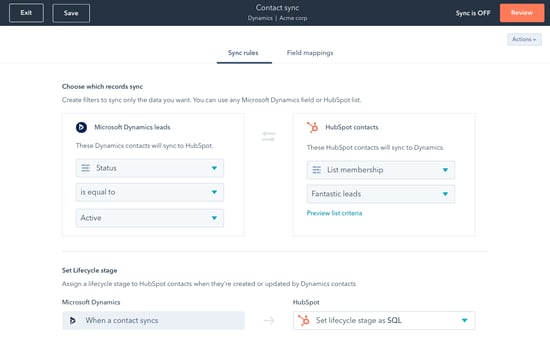
Data Integration
Data Lifecycle Management
Customer Data Platforms and Data Warehouses
Data Management Software
Master Data Management Software
SAP
Ataccama
Storage Management Software
Amazon Elastic Block Store
Google Drive
Microsoft OneDrive
RevOps
Integration Software
Operations Hub
Zapier
Automate.io
Benefits of Investing in Data Management
Understanding Your Most Profitable Customers
Evaluating Customer Acquisition Channels
Seeing Your Full Buying Cycle
Other Data Management Concepts
Data Management is for Everyone


Originally published Jul 28, 2021 2:00:00 PM, updated July 29 2021
Intervention By Design Data Management Tool
Source: https://blog.hubspot.com/website/data-management
Posted by: cartiertoloses.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Intervention By Design Data Management Tool"
Post a Comment